The parts manufacturing industry plays a pivotal role in the advancement of modern technology, with a projected global market value of over $500 billion by 2025 according to recent industry reports. The selection of the appropriate manufacturing process is critical for ensuring that projects meet their performance criteria and budget constraints. As manufacturing technology evolves, stakeholders must navigate a myriad of options that can impact production efficiency, material properties, and turnaround times.
Expert in the field, Dr. Emily Johnson, a renowned mechanical engineer, emphasizes, "Choosing the right parts manufacturing process is not just about cost; it's about delivering precision and performance." Her insights highlight the importance of understanding the capabilities of different manufacturing techniques, whether it be additive manufacturing, machining, or injection molding. Each process has its unique advantages and limitations, and therefore requires careful consideration based on the specific needs of the project at hand.
In an increasingly competitive landscape, companies that leverage the right parts manufacturing techniques can gain a substantial edge, driving innovation and enhancing product quality. This guide aims to provide valuable insights into choosing the right manufacturing process tailored to your specific project needs, ensuring optimal outcomes in both quality and efficiency.

When selecting the appropriate parts manufacturing process for your project, it's essential to understand the diverse options available and how they align with your project requirements. Among the most widely used methods are machining, injection molding, additive manufacturing, and sheet metal fabrication. Each process has its unique advantages and is suited for different types of materials, complexities, and production volumes. For example, machining is ideal for creating precise components from various metals or plastics, while injection molding excels in producing large quantities of intricate shapes efficiently.
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, offers unmatched design flexibility, enabling the production of complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional methods. This process is particularly valuable for prototyping and low-volume production runs. On the other hand, sheet metal fabrication is commonly employed for projects that require durability and strength, as it allows for the shaping and assembly of metal sheets into functional parts. Understanding these processes, along with their material compatibility and production capabilities, is crucial for making informed decisions that meet your project’s specific demands.
| Manufacturing Process | Material Compatibility | Typical Applications | Cost Efficiency | Lead Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Machining | Metals, Plastics | Complex Geometries, Prototypes | Moderate | 1-3 weeks |
| Injection Molding | Plastics | High-Volume Production, Consumer Goods | High for large runs | 2-4 weeks |
| 3D Printing | Plastics, Metals | Prototyping, Custom Parts | Moderate to High | 1-2 weeks |
| Stamping | Metals | Automotive Parts, Appliances | High for large volumes | 1-3 weeks |
| Casting | Metals | Heavy Machinery, Engine Components | Moderate to High | 2-6 weeks |
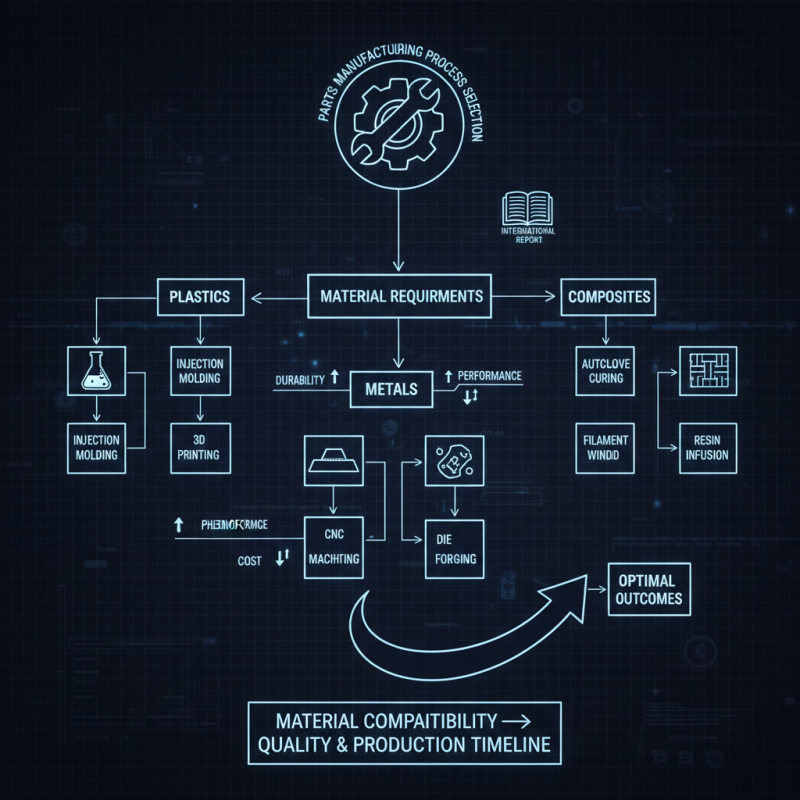
When selecting the right parts manufacturing process for your project, several key factors must be considered to ensure optimal outcomes. First, the material requirements play a crucial role. According to a report by the ASTM International, the choice of material can affect durability, performance, and cost. Different processes, such as injection molding or CNC machining, may be more suitable depending on whether you need plastics, metals, or composites. Evaluating the material compatibility not only influences the quality of the parts but also impacts the overall production timeline.
Another significant factor is the complexity of your design. Highly intricate geometries may require advanced manufacturing techniques like additive manufacturing, which allows for greater design freedom. A survey by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers noted that 75% of manufacturers have turned to 3D printing to reduce lead time for complex components. Therefore, understanding the capabilities and limitations of each process is essential in aligning your design requirements with manufacturing capabilities.
Tips: Always prototype early in the process to assess the feasibility of manufacturing methods. Additionally, collaborate with manufacturing partners who have experience in the specific techniques relevant to your project. This proactive approach can identify potential issues before full-scale production begins, ensuring efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Engaging with industry experts can also provide insights into which manufacturing processes yield the best results for your specific application.
The choice between additive and subtractive manufacturing techniques is pivotal in optimizing the production process for any project. Additive manufacturing, often known as 3D printing, builds parts layer by layer from digital models. This method allows for complex geometries and customization, as it can produce intricate designs that would be impossible or prohibitively expensive to create with traditional methods. Moreover, additive manufacturing typically results in minimal waste, since materials are added only where needed.
Conversely, subtractive manufacturing involves removing material from a solid block to achieve the desired shape. Techniques such as milling and turning are commonly used in this process. While subtractive methods tend to be more efficient for producing larger quantities of standardized parts, they can lead to significant material waste. One of the key advantages of subtractive manufacturing is its capability to achieve high precision and surface finish, ideal for applications where dimensional accuracy is critical. Ultimately, the decision between these techniques should consider factors such as project requirements, material types, and cost constraints, ensuring that the most appropriate manufacturing method is selected for optimal results.

When selecting a manufacturing process for your project, it's crucial to thoroughly evaluate the three primary factors: cost, speed, and quality. According to a study by the Manufacturing Institute, companies often find themselves balancing these elements to optimize production while maintaining profitability. For instance, a report from Deloitte indicates that 75% of manufacturers prioritize cost effectiveness, yet nearly 70% acknowledge that quality impacts long-term customer satisfaction. Therefore, making informed decisions requires a careful examination of each factor.
Cost is often the first consideration when choosing a manufacturing process. A simplistic approach may focus solely on initial expenses, but hidden costs can arise in labor, material waste, and overhead. On the other hand, a speedy manufacturing process—such as additive manufacturing—can significantly reduce lead times, yet may not be the most cost-effective option in every scenario. It's essential to conduct a thorough cost analysis that includes not just production costs, but also expected product life and market demand.
**Tips:** One effective strategy is to create a cost-benefit analysis that compares different manufacturing processes based on their projected total costs and expected quality outcomes. Additionally, consider how speed may influence your ability to meet market demands; faster production can provide a competitive edge. Lastly, invest in quality control measures early in the production process to ensure that high standards are maintained, which can ultimately save costs related to rework and defects.
In various industries, choosing the right parts manufacturing process can significantly affect a project’s outcome. For instance, the aerospace sector relies heavily on additive manufacturing for producing lightweight components. According to a report by Markets and Markets, the aerospace additive manufacturing market is projected to grow from $1.5 billion in 2020 to $6.8 billion by 2025, showcasing the increasing reliance on 3D printing technologies to meet complex design requirements while reducing material waste.
 In the automotive industry, companies have successfully implemented injection molding processes to streamline production and enhance efficiency. A study from the American Society of Mechanical Engineers indicates that injection molding can reduce manufacturing costs by up to 30% compared to traditional machining methods. This shift has allowed manufacturers to produce high volumes of precision parts quickly, adapting to the fast-paced demands of modern vehicle production. As evidenced by case studies, the ability to select the appropriate manufacturing process not only drives innovation but also contributes significantly to operational success across diverse industries.
In the automotive industry, companies have successfully implemented injection molding processes to streamline production and enhance efficiency. A study from the American Society of Mechanical Engineers indicates that injection molding can reduce manufacturing costs by up to 30% compared to traditional machining methods. This shift has allowed manufacturers to produce high volumes of precision parts quickly, adapting to the fast-paced demands of modern vehicle production. As evidenced by case studies, the ability to select the appropriate manufacturing process not only drives innovation but also contributes significantly to operational success across diverse industries.