Machine fabrication is a transformative process in modern manufacturing. It involves creating parts and structures from raw materials using machines. According to Dr. Emily Carter, a leading expert in machine fabrication, “The process revolutionizes how industries approach production efficiency.” This technology plays a vital role in sectors like automotive, aerospace, and construction.
The intricate details of machine fabrication can be fascinating. This process not only boosts productivity but can also present challenges. Understanding how these machines operate is crucial for any company. Many firms struggle with integrating advanced machinery into their existing workflows. The complexity of machine fabrication often requires ongoing training and adaptability.
Moreover, as industries evolve, the question remains: how can they leverage machine fabrication effectively? Success in the field demands a balance between innovation and traditional methods. Companies must reflect on their practices to stay competitive. Machine fabrication is more than just a technique; it’s an evolving paradigm in manufacturing we must critically analyze.

Machine fabrication is a critical process in manufacturing. It involves shaping and assembling materials into various forms. This technique can utilize metals, plastics, or other resources. Fabrication often combines cutting, welding, and machining. Each method plays a vital role in creating accurate components.
The definition of machine fabrication can vary. Essentially, it refers to the creation of structures through machinery. Many industries depend on this process for production. Difficulties can arise when precision is required. Factors like temperature fluctuations can affect materials and methods. Thus, understanding machinery and material behavior is vital.
Errors in fabrication can lead to significant setbacks. Miscalculations during the design phase can result in waste. It’s crucial to inspect and ensure quality at every stage. Continuous learning and adaptation are needed to improve techniques. Engaging in discussions about challenges can enhance the process, leading to better practices.
Machine fabrication encompasses a range of processes, transforming raw materials into finished products. Key processes include machining, welding, and assembly. Each step requires precision and skill. According to a recent industry report, around 60% of fabrication failures are due to poor machining practices. This highlights the importance of consistency in quality control.
Machining is the most common process. It involves removing material from a workpiece to achieve desired dimensions and surface finish. Techniques like turning, milling, and drilling are prevalent. An estimated 30% of machining time is wasted on setup and tool changes. Optimizing these aspects can enhance efficiency significantly.
Welding is equally crucial. This process joins different parts together using heat. However, improper techniques can lead to weaknesses in the final structure. Research shows that around 50% of welding defects arise from inadequate training. Investing in better training programs can mitigate these risks.
Assembly follows, requiring meticulous attention to detail. Each component must fit together seamlessly to ensure functionality. Even minor oversights can lead to significant failures later on.
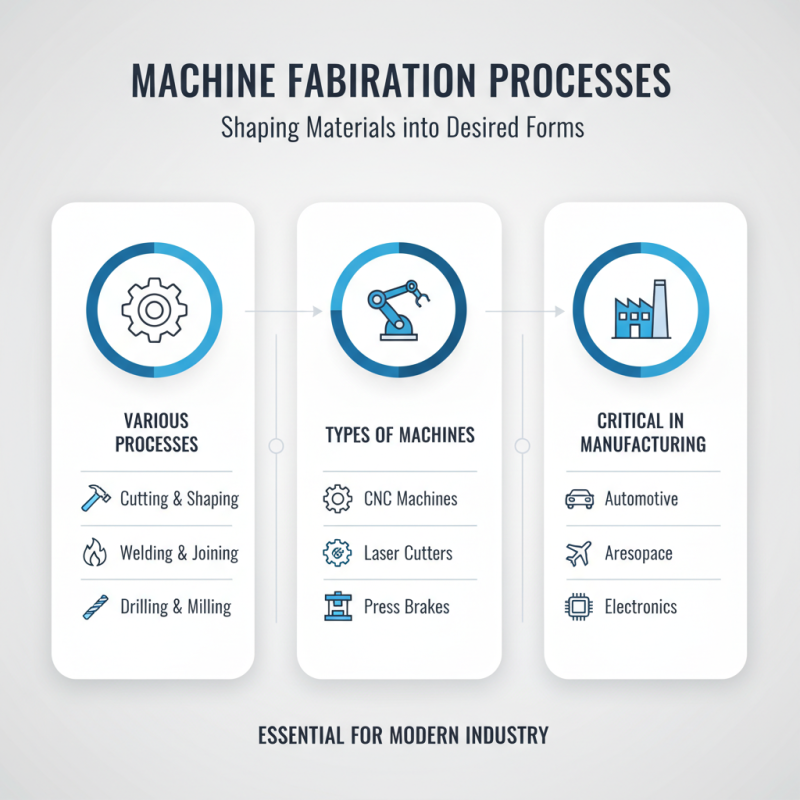
Machine fabrication involves various processes that shape materials into desired forms. The types of machines used in fabrication can vary widely. Each machine serves a unique purpose, yet they are critical in various manufacturing sectors.
One common type is the CNC milling machine. It cuts materials precisely, often from blocks of metal or plastic. This machine can create complex parts with minimal human input. However, it requires skilled operators who understand programming. A slight error in commands can lead to significant waste. It is a reminder of how delicate the manufacturing process can be.
Another key player is the laser cutter. This machine uses focused light to slice through materials. It is efficient and can achieve intricate designs. However, the initial setup time can be lengthy. Adjustments may also be needed for different materials. While laser cutting is admired for its precision, it highlights the struggles with material compatibility and machine learning curves. These challenges remind us to continually refine our techniques for better outcomes.
Machine fabrication plays a crucial role in various industries. It involves the use of machines to create parts or products from raw materials. This technique is prevalent in manufacturing sectors, such as automotive and aerospace. Here, precision is fundamental. Even a minor error can lead to significant issues later in the production line.
In the construction industry, machine fabrication helps to make steel beams and frames. These components are vital for structural integrity. Without precise fabrication, buildings could become unsafe or unfit for use. There are challenges, such as the need for skilled operators and maintenance of machines. If not addressed, these challenges can lead to delays and increased costs.
Moreover, the technology is evolving rapidly. New methods may soon replace traditional practices. Industries must adapt to stay competitive. However, not every company is ready to invest in the latest technologies. This hesitation can limit growth opportunities. Overall, machine fabrication continues to be an essential aspect of industrial processes. Its applications are broad, but the pursuit of quality and efficiency remains a constant challenge.
The future of machine fabrication technology is poised for significant changes. By 2027, the global market for machine fabrication is expected to reach approximately $200 billion. This growth highlights the increasing reliance on advanced fabrication methods. Automation and artificial intelligence (AI) are driving forces behind this trend. They enhance precision and efficiency in manufacturing processes.
However, challenges remain. Integrating new technology requires investment and retraining of the workforce. As companies adopt AI and robotics, the risk of job displacement rises. In 2022, a report indicated that nearly 15% of the workforce in manufacturing may face job transformation due to these advancements. The need for skilled labor in managing sophisticated machines will expand. Training programs must evolve to address these demands.
Sustainability is another crucial factor. The industry is pressured to minimize waste and energy consumption. Innovations in recycling materials and energy-efficient machinery are gaining traction. A 2023 report noted that companies adopting green technologies saw a 25% reduction in costs. As machine fabrication technology advances, balancing profitability and sustainability will remain a complex challenge. The future is bright, yet it demands careful consideration.