In the ever-evolving landscape of welding manufacturing, efficiency emerges as a key focus for reducing costs and enhancing productivity. A recent study by the American Welding Society noted that the industry is projected to grow by 4% annually through 2026. This growth emphasizes the need for innovative techniques that optimize resources and minimize waste.
Expert John Smith, a renowned figure in welding manufacturing, once stated, "Embracing new technologies is essential for staying competitive in this industry." His insight reflects the pressing demand for advancements in welding processes, such as automation and real-time monitoring systems. Implementing these techniques can significantly increase output and quality, yet many companies still struggle to adapt.
Challenges remain in fully integrating these advanced methods into existing workflows. Not all manufacturers have the resources or knowledge to implement these changes effectively. As the sector seeks to modernize, the balance between traditional practices and innovative approaches requires careful consideration. The future of welding manufacturing hinges on this delicate transition.

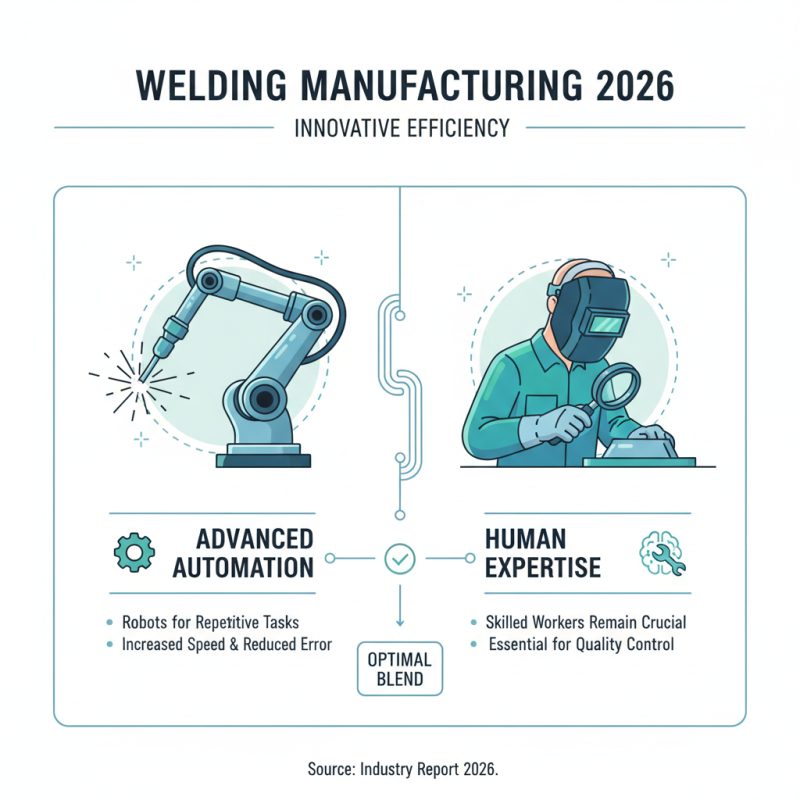
Welding manufacturing techniques in 2026 focus on innovative approaches to enhance efficiency. Advanced automation plays a significant role. Robots are increasingly used for repetitive tasks. They improve speed and reduce human error. However, relying too heavily on automation can have drawbacks. Skilled workers are still essential for quality control.
Another aspect is the integration of new materials. Lightweight alloys and composites are gaining popularity. These materials can improve performance but may require different welding techniques. Not all welders are trained for this shift. This gap can lead to inconsistencies in the final product.
Continuous training for workers is crucial. Implementing feedback loops helps identify areas for improvement. Many companies overlook this aspect, resulting in wasted resources. An effective strategy involves regular workshops and skill assessments. It addresses the learning curve associated with new technologies and methods. In 2026, embracing these techniques will be vital for competitiveness.
Welding efficiency in modern manufacturing is shaped by several key factors. One major aspect is the choice of welding technique. Different methods yield varying levels of productivity and quality. For instance, MIG welding often provides quicker results than TIG welding, but with some loss in precision. Manufacturers must weigh speed against quality for their specific projects.
Another factor is equipment maintenance. Well-maintained equipment operates smoothly, reducing downtime. If tools are neglected, they may lead to defects. A small fault can escalate into larger issues. Workers need to stay vigilant, ensuring everything is in optimal condition. Training is crucial too. Skilled operators can adapt to challenges promptly, but inexperienced hands might struggle. Companies should invest in regular training sessions for their workforce.
Additionally, environmental conditions play a role. Temperature, humidity, and even air quality can affect welding outcomes. Teams need to monitor their work environments. Sometimes external factors throw a wrench in the operations. Unexpected challenges arise, requiring quick adjustments. Reflecting on these elements can help enhance overall efficiency, ensuring a smoother welding process.
Innovative welding technologies are transforming production processes in remarkable ways.
Automation and robotics are revolutionizing the industry. These technologies enhance precision and allow for faster production rates.
Advanced techniques like laser welding and 3D printing offer new capabilities. They enable welders to create complex designs with minimal waste.
This shift is not just about speed; it's also about quality.
Tips: Embrace automation to increase consistency. Develop a training program for your workers on new technologies.
This adaptation is crucial, yet it requires time and effort.
Consider the challenge of integrating new systems with existing ones. Older machines may not easily accommodate these changes.
Testing and calibration become essential steps in the process. Moreover, staying updated on emerging trends is vital.
The welding landscape is rapidly evolving.
Finally, always review your current practices. Identify bottlenecks or inefficiencies.
Regular assessments can lead to significant improvements.
A commitment to innovation will keep businesses competitive in this fast-paced market.
The landscape of welding techniques has evolved significantly. Traditional methods, such as MIG and TIG welding, have been the backbone of many industries for years. They are reliable and generally easy to learn. However, they come with limitations. For instance, they can be time-consuming and less efficient for large-scale projects. Some welders might also struggle with consistency.
On the other hand, advanced welding methods like laser welding and friction stir welding are transforming the industry. These techniques often provide faster processing times and improved joint quality. They can handle complex geometries that traditional methods cannot. However, the equipment can be expensive and challenging to master. Not all welders may have access to the necessary training, creating a gap in skill levels and limits the benefits of these advanced techniques.
The choice between traditional and advanced methods requires careful consideration. Each has strengths and weaknesses that can affect productivity and quality. Companies need to weigh these factors before making a decision. Balancing cost-efficiency with technological advancement is crucial for future growth in the welding sector.
Welding techniques have evolved significantly, but challenges still remain. Implementing efficient practices requires understanding the workflow and techniques that best suit specific projects. One common issue is poor planning. Without clear blueprints, time and materials can be wasted. Employing digital modeling can help visualize the end project. This foresight minimizes errors during the actual welding process.
Another important practice is proper training. Everyone on the team must understand the tools and techniques being used. Regular workshops can keep skills sharp. However, training must adapt to new technologies. This is a gap many companies overlook. Investing in education not only improves efficiency but can also reduce rework due to errors.
Lastly, equipment maintenance is often disregarded. Well-maintained machines run smoother and produce better welds. Scheduling routine check-ups can prevent unexpected breakdowns. Moreover, feedback from welders can guide which tools need upgrades or repairs. Balancing all these factors is crucial for truly efficient welding operations. Continuous reflection on processes can lead to improvement and innovation, ensuring long-term success.
| Technique | Efficiency Benefits | Application Industry | Implementation Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Robotic Welding | Increased speed and precision, reduced waste | Automotive, Aerospace | High initial investment, low operational costs |
| Laser Welding | Minimal thermal distortion, high strength welds | Electronics, Medical Devices | Medium to high cost depending on setup |
| TIG Welding | High quality, versatility in materials | Construction, Pipefitting | Moderate initial cost, skill-dependent |
| MIG Welding | Faster welding speeds, easy to learn | Manufacturing, Repair | Low cost and high usability |
| Friction Stir Welding | Joint strength, no filler material required | Shipbuilding, Aerospace | High equipment cost, long-term savings |





